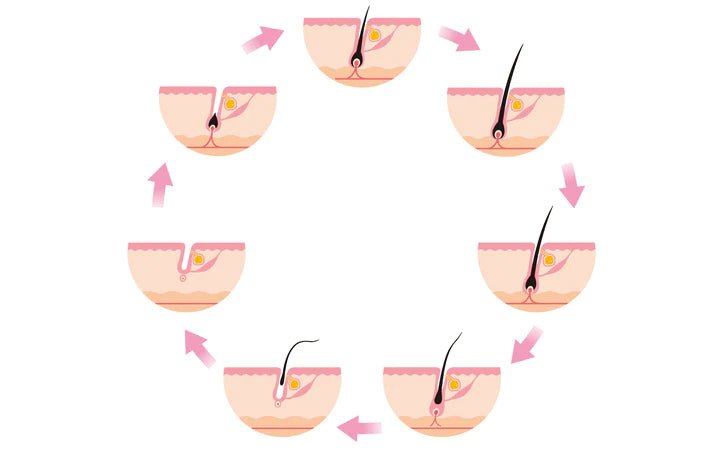
Hair growth is a complex process that occurs in three phases: the anagen phase, the catagen phase, and the telogen phase.
-
Anagen phase: The anagen phase is the active growth phase of hair. During this phase, the hair follicle produces hair cells rapidly, and the hair grows longer. The length of the anagen phase varies between individuals and can last anywhere from two to six years.
-
Catagen phase: The catagen phase is a transitional phase between the anagen and telogen phases. It lasts for around two weeks, during which the hair follicle shrinks and detaches from the blood supply, causing the hair to stop growing.
-
Telogen phase: The telogen phase is the resting phase of hair growth, lasting for around three months. During this phase, the hair follicle is at rest, and the old hair falls out, making room for new hair to grow in the anagen phase.
After the telogen phase, the hair follicle returns to the anagen phase, and the cycle begins again. The growth rate of hair can vary depending on factors such as age, genetics, and overall health. The average rate of hair growth is around half an inch per month, but this can vary widely between individuals.