Alopecia is a medical term used to describe the partial or complete loss of hair, often from the scalp, but it can also affect hair on other parts of the body. There are several types of alopecia, each with its own causes and characteristics. Some of the most common types of alopecia include:
-
Alopecia Areata: This is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It often results in round, smooth bald patches on the scalp or other hair-bearing areas of the body.
-
Androgenetic Alopecia: Also known as male-pattern or female-pattern baldness, this type of alopecia is the most common cause of hair loss. It is hereditary and typically occurs as people age. In men, it often leads to a receding hairline and balding on the top of the head, while in women, it can cause thinning of the hair.
-
Alopecia Totalis: This is a more severe form of alopecia areata in which all of the hair on the scalp is lost.
-
Alopecia Universalis: This is an even more extensive form of alopecia areata, resulting in the loss of all body hair, including eyelashes, eyebrows, and hair on other parts of the body.
-
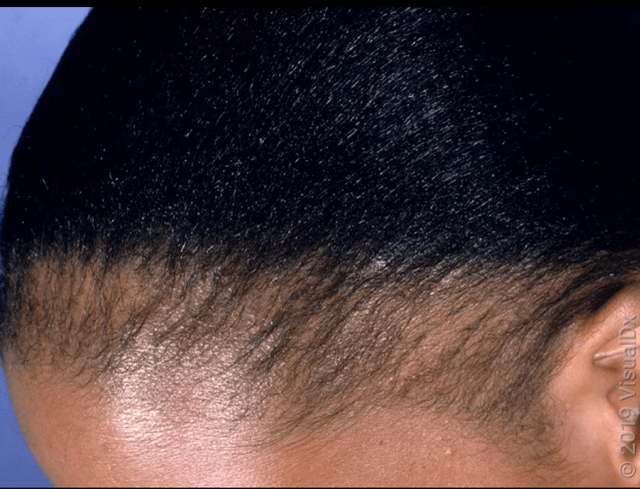
Traction Alopecia: This type of hair loss occurs when hair is pulled too tightly for extended periods, often due to hairstyles like tight ponytails, braids, or cornrows. It can lead to hair breakage and hair loss in affected areas.
-
Scarring Alopecia: This refers to hair loss that results from damage to hair follicles and is often accompanied by scarring of the scalp. Various factors, including inflammation, infections, and certain skin conditions, can cause scarring alopecia.
-
Telogen Effluvium: This type of hair loss is usually temporary and occurs when a larger-than-normal proportion of hair follicles enters the resting (telogen) phase of the hair growth cycle. It can be triggered by various factors, such as stress, illness, childbirth, medications, or dietary deficiencies.
The treatment for alopecia depends on its type and underlying cause. Some forms of alopecia may resolve on their own, while others may require medical intervention, such as corticosteroid treatments, immunosuppressants, or hair transplant surgery. It's essential to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan if you're experiencing hair loss.