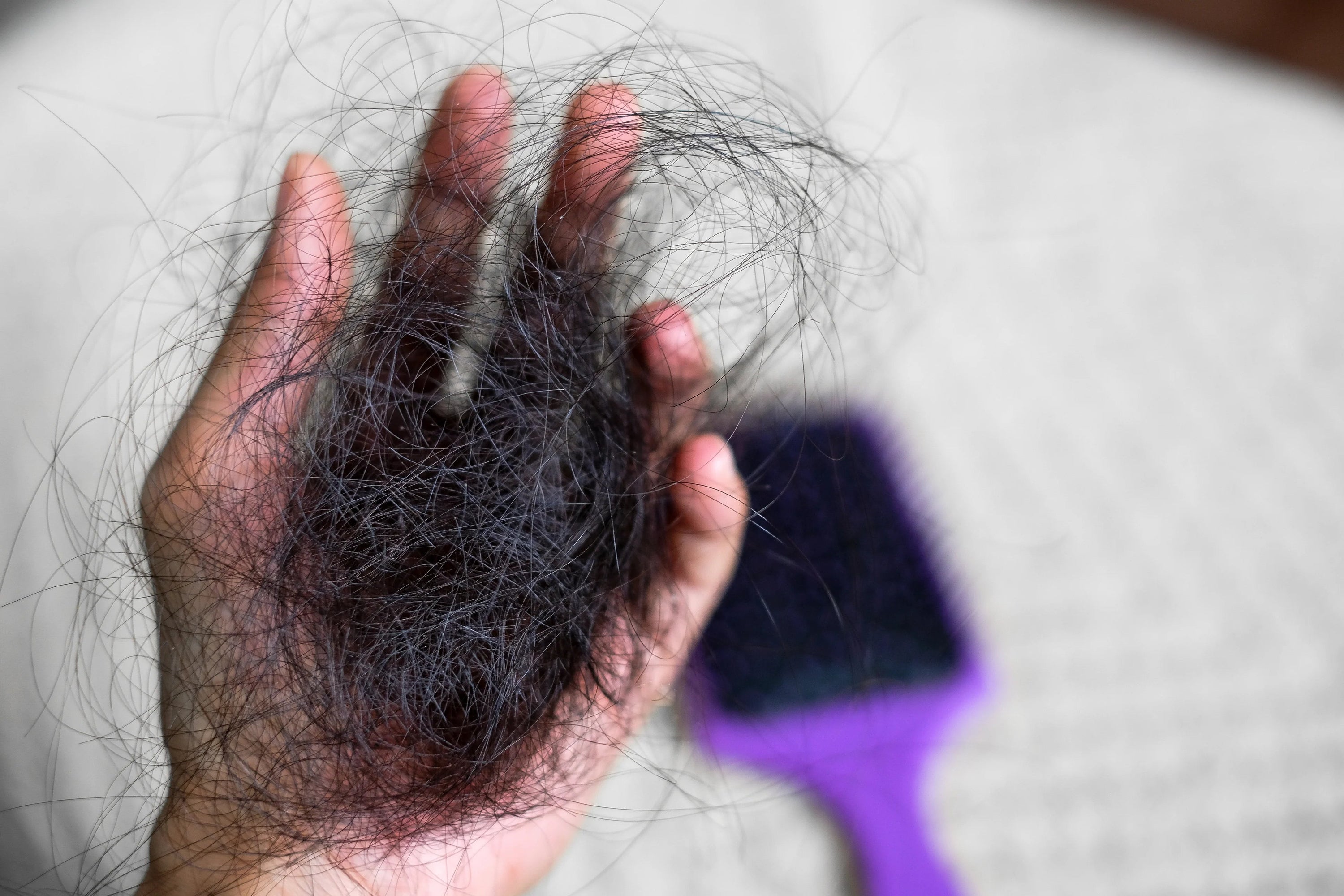
Alopecia is a medical condition characterized by the partial or complete loss of hair on the scalp or other parts of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. There are several types of alopecia, including:
- Alopecia areata: This is the most common form, causing patches of hair loss on the scalp or other areas of the body.
- Alopecia totalis: It involves the complete loss of hair on the scalp.
- Alopecia universalis: It results in the loss of all body hair, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and hair on the scalp.
The exact cause of alopecia is not yet fully understood, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder, meaning the immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells. Other factors, such as genetics and environmental triggers, may also play a role.
While there is no cure for alopecia, several treatment options are available to help manage the condition and promote hair regrowth. These include:
- Medications: Corticosteroids, such as topical creams or injections, can be used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system response in the affected areas.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This over-the-counter medication can be applied topically to promote hair growth.
- Anthralin: It is a topical medication that alters the immune function in the affected area.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment involves stimulating hair growth by inducing an allergic reaction in the affected area.
In addition to medical treatments, there are some lifestyle changes and supportive measures that may help individuals with alopecia:
- Wearing wigs, scarves, or hats: These can help conceal hair loss and protect the scalp from sunlight and other external factors.
- Cosmetics: Some people use cosmetics, such as eyebrow pencils or eyeliner, to create the appearance of eyebrows or eyelashes.
- Emotional support: Living with hair loss can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups can be helpful.
- Stress management: Stress may exacerbate hair loss, so finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise or relaxation techniques, can be beneficial.
It's important to consult with a healthcare professional, preferably a dermatologist or a specialist in hair disorders, to discuss the specific type and severity of alopecia and determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your situation.